
Basic setup
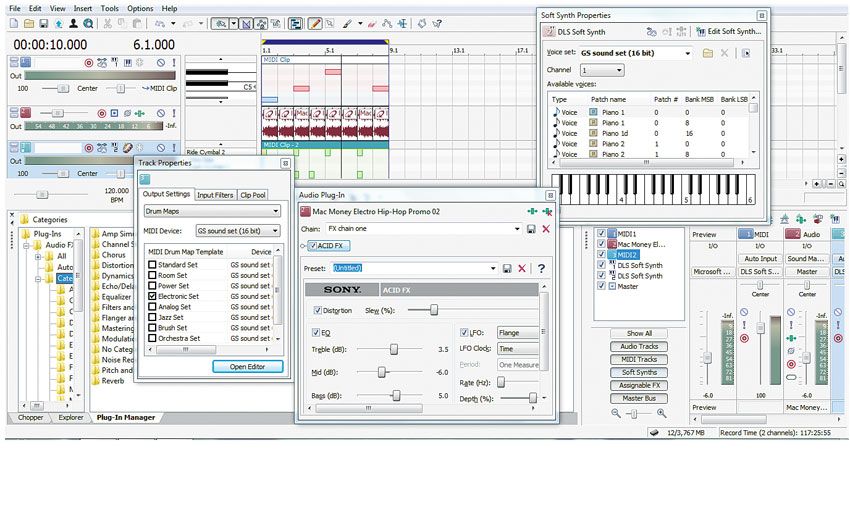
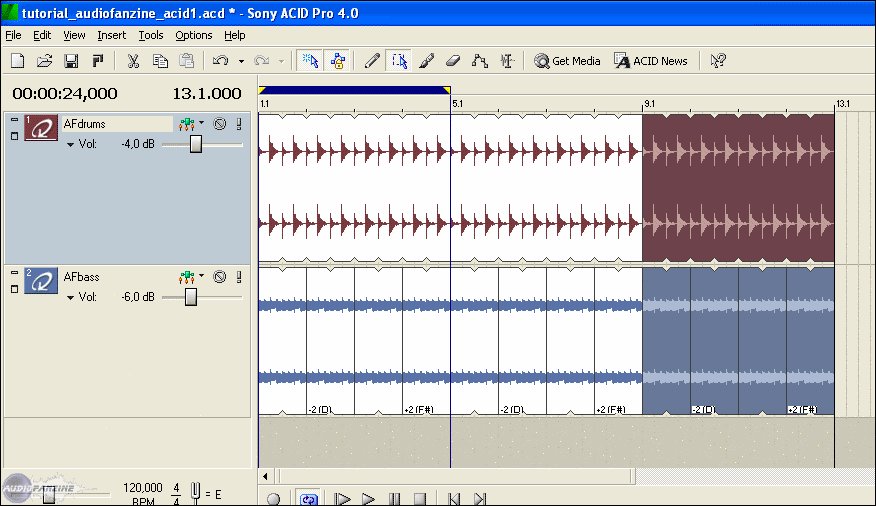
ACID Music Studio is a software solution that comes bundled with the necessary tools to create, record, edit audio tracks, and more. The user interface of the program can look a bit confusing. Sony ACID Music Studio is a Commercial software in the category Audio & Multimedia developed by Koch Media Deutschland GmbH. It was checked for updates 94 times by the users of our client application UpdateStar during the last month. The latest version of Sony ACID Music Studio is 8.0, released on. The Sony ACID Music Studio 10 is the ideal gateway to total music production. It's easy-drop a beat on the timeline and dig in. Put the software to work and take advantage of all the production tools you need to make the music you've always wanted to hear. Acid Pro (often stylized ACID) is a professional digital audio workstation (DAW) software program currently developed by Magix Software.It was originally called Acid pH1 and published by Sonic Foundry, later by Sony Creative Software as Acid Pro, and since spring 2018 by Magix as both Acid Pro and a simplified version, Acid Music Studio.Acid Pro 8 (the current version as of 2019) supports 32. ACID Music Studio displays a graphic interface similar to a true musical recording studio, ideal for people wanting to compose music. With this program you can obtain audio from diferents sources: microphone, aux and line in inputs, etc. Creating a new track for each of the input signals.
In this setup, an audio source is connected to an input on your sound card, and your powered speakers are connected to a Line Out output. You could connect a computer microphone to your sound card’s Mic In input, or you can connect line-level outputs from a tape deck or other source to a Line In input.
Basic setup with mixer/preamplifier
In this setup, your speakers and audio source are connected to a mixer or preamplifier. The mixer/preamplifier is then connected to Line In and Line Out connections on your sound card.
If you’re recording from a turntable, use a phono preamplifier between your turntable’s output and your sound card’s line input. Most turntables’ outputs are phono-level (rather than line-level) outputs. Phono-level outputs are quieter than line-level outputs and have special equalization applied. A phono preamplifier will convert the phono-level signal to a line-level signal that you can record.
Digital input/output with MIDI synchronization
In this setup, an audio source with digital input/output is connected to a sound card with digital input and outputs. Dashed lines represent a sync connection from your audio source to a MIDI timecode converter to a MIDI card.
Before you start recording, you’ll need to verify that your sound card’s recording inputs are active.
Ensure all cables are connected and that your audio source is generating a signal.
Select the Arm for Record buttons on the tracks where you want to record. Arming a track enables it for recording.
When a track is armed, the track meter displays the track’s level. If input monitoring is not on, the meter displays the level of your input source. If input monitoring is turned on, the meter shows the level of the input source plus the track effects chain.
To choose your recording input, click the Record Device Selector button , choose an audio device from the menu, choose Mono or Stereo from the submenu, and then choose an input.
Adjust your recording levels:
If your audio device provides a console application to adjust levels, open the application and adjust its gain controls while monitoring the peak meters on the Meters tab in the recording dialog. Adjust the gain controls in the console application so ACID receives a strong signal with no clipping.
For more information about using your sound card and its console application, please refer to the manufacturer’s documentation.
If you’re using your Windows sound card, perform the following steps to open the recording controls:
Double-click the speaker icon in your system tray to open the Volume Control window.
From the Options menu, choose Properties.
Click the Recording radio button and click OK.
Select (or unmute) the device from which you want to record.
Adjust the Volume faders for the selected device and for the Master Record level while monitoring the recording meters in the ACID Record dialog.
For example, if you want to record from an audio CD in your CD-ROM drive, the CD Mute check box should not be selected, and the CD and Master Record Volume faders must be adjusted so ACID receives a strong signal with no clipping.
If you have a sound card with multiple inputs and outputs, you can record multiple tracks at once. Repeat steps 2 through 4 to choose an input device and set levels for each track.
Click the Record button below the timeline when you’re ready to start recording.
For more information about recording audio, please see Recording Audio.
This topic provides general guidelines to help you record sound from an external source using ACID software. Your specific hardware may vary. Please refer to your hardware documentation for more information.
If you’re recording from a turntable, use a phono preamplifier between your turntable’s output and your sound card’s line input. Most turntabl
es’ outputs are phono-level (rather than line-level) outputs. Phono-level outputs are quieter than line-level outputs and have special equalization applied. A phono preamplifier will convert the phono-level signal to a line-level signal that you can record.
What do you want to do?
Connect an audio source to your sound card’s input
Choose an input device and adjust levels
Recording Audio from an External Source
Basic setup
In this setup, an audio source is connected to an input on your sound card, and your powered speakers are connected to a Line Out output. You could connect a computer microphone to your sound card’s Mic In input, or you can connect line-level outputs from a tape deck or other source to a Line In input.
Basic setup with mixer/preamplifier
In this setup, your speakers and audio source are connected to a mixer or preamplifier. The mixer/preamplifier is then connected to Line In and Line Out connections on your sound card.
If you’re recording from a turntable, use a phono preamplifier between your turntable’s output and your sound card’s line input. Most turntables’ outputs are phono-level (rather than line-level) outputs. Phono-level outputs are quieter than line-level outputs and have special equalization applied. A phono preamplifier will convert the phono-level signal to a line-level signal that you can record.
Digital input/output with MIDI synchronization
In this setup, an audio source with digital input/output is connected to a sound card with digital input and outputs. Dashed lines represent a sync connection from your audio source to a MIDI timecode converter to a MIDI card.
Before you start recording, you’ll need to verify that your sound card’s recording inputs are active.
Ensure all cables are connected and that your audio source is generating a signal.
Select the Arm for Record buttons on the tracks where you want to record. Arming a track enables it for recording.
When a track is armed, the track meter displays the track’s level. If input monitoring is not on, the meter displays the level of your input source. If input monitoring is turned on, the meter shows the level of the input source plus the track effects chain.
To choose your recording input, click the Record Device Selector button , choose an audio device from the menu, choose Mono or Stereo from the submenu, and then choose an input.
Adjust your recording levels:
If your audio device provides a console application to adjust levels, open the application and adjust its gain controls while monitoring the peak meters on the Meters tab in the recording dialog. Adjust the gain controls in the console application so ACID receives a strong signal with no clipping.
For more information about using your sound card and its console application, please refer to the manufacturer’s documentation.
If you’re using your Windows sound card, perform the following steps to open the recording controls:
Double-click the speaker icon in your system tray to open the Volume Control window.
From the Options menu, choose Properties.
Click the Recording radio button and click OK.
Select (or unmute) the device from which you want to record.
Adjust the Volume faders for the selected device and for the Master Record level while monitoring the recording meters in the ACID Record dialog.
For example, if you want to record from an audio CD in your CD-ROM drive, the CD Mute check box should not be selected, and the CD and Master Record Volume faders must be adjusted so ACID receives a strong signal with no clipping.
If you have a sound card with multiple inputs and outputs, you can record multiple tracks at once. Repeat steps 2 through 4 to choose an input device and set levels for each track.
Click the Record button below the timeline when you’re ready to start recording.
For more information about recording audio, please see Recording Audio.
This topic provides general guidelines to help you record sound from an external source using ACID software. Your specific hardware may vary. Please refer to your hardware documentation for more information.
If you’re recording from a turntable, use a phono preamplifier between your turntable’s output and your sound card’s line input. Most turntabl
es’ outputs are phono-level (rather than line-level) outputs. Phono-level outputs are quieter than line-level outputs and have special equalization applied. A phono preamplifier will convert the phono-level signal to a line-level signal that you can record.